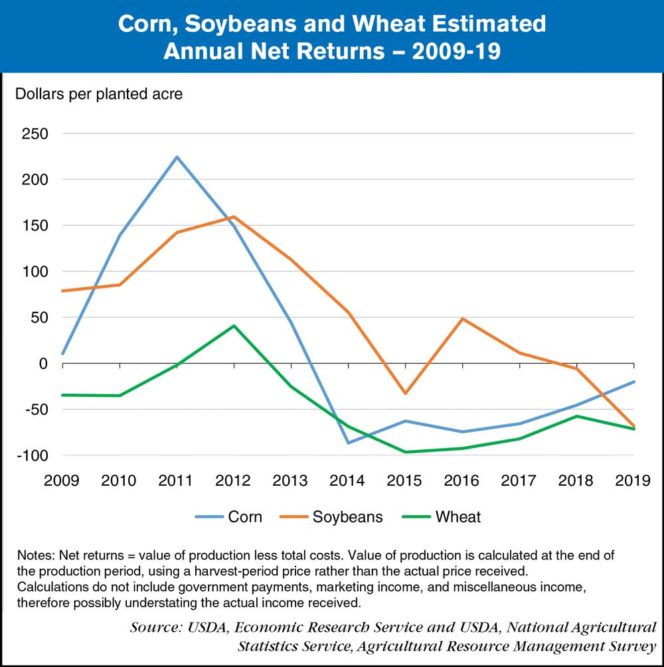
Producers of some of the U.S. major field crops have struggled to cover total costs of production over the past decade. The Economic Research Service’s (ERS) Commodity Costs and Returns product estimates this gap or surplus in the calculation of the value of production less total costs, referred to here as net returns. Total costs comprise operating costs, which include expenses such as fertilizer, seed and chemicals, and allocated overhead (economic) costs, which include unpaid labor, depreciation, land costs and other opportunity costs. Although revenue from selling crops can typically cover operating costs each year, net returns have often been negative. This suggests that, in some cases, allocated overhead costs are not covered.
Corn’s net returns increased early in the decade, primarily due to a boom in the production of corn-based ethanol. Corn yields and acreage remained high after the boom, leaving supply high and leading, in part, to lower prices and returns over time. Net returns for soybeans shadowed those for corn during the ethanol boom, remaining higher than those for corn up until 2018. Wheat prices and returns also declined, due to strong international competition and several high-yield domestic crops. This chart is derived from data collected from the ERS Commodity Costs and Returns data product. Its data can also be viewed via ERS’s interactive data visualization product, U.S. Commodity Costs and Returns by Region and by Commodity.